Set Up: Understanding the Visitors Metrics in cPanel
The Visitor interface displays detailed information about the 1,000 most recent visits to your website.
This information is important as it helps you learn about your visitors and audience, and monitor frequent visitors so you can adjust your website content to fit their needs. You can also use the information to locate and fix errors on your website, such as missing pages or broken links.
To view the Visitors metrics:
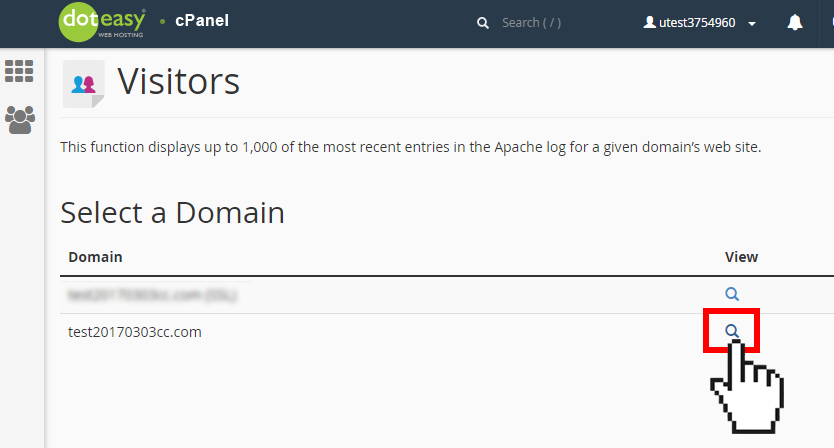
- Click on Visitors under Metrics in cPanel.

- Click on the
 icon next to the domain name you want to view Visitors metrics. This will open the Visitors log interface.
icon next to the domain name you want to view Visitors metrics. This will open the Visitors log interface.

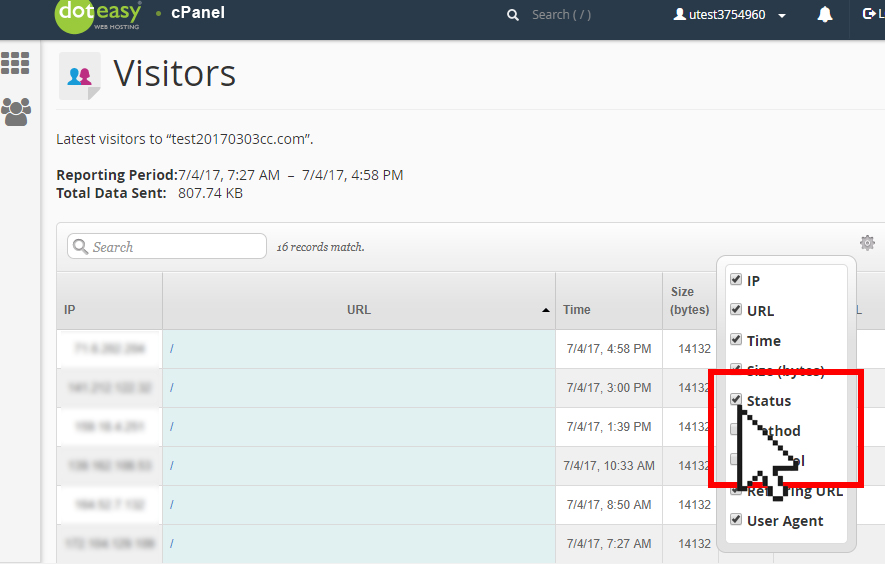
- By default, the interface displays the following information:

Detail Description IP The visitors’ IP address Time The time when the visitor accessed your website Size The amount of data that the server sent to the visitor for this resource Referring URL The web address from which the visitor navigated to the resource User Agent The browser that the visitor used to access your website - Click on the
 icon to select additional data to display.
icon to select additional data to display.

- Select the additional data you want to display by clicking on the checkbox next to the option(s).

Option Description Status The HTTP code indicates whether the resource loaded successfully or resulted in an error Method The request-response between the client and server (for example, GET or POST) Protocol The version of HTTP that the server used to serve the resource to the visitor
Status HTTP Codes
HTTP codes describe the status of a URL when a visitor attempts to access it. HTTP codes include error messages that describe the problems that visitors encounter. The codes are three-digit numbers.
The following table represents the five classes of HTTP codes, divided by the first digit:
| First Digit | Description |
| 1, 2, or 3 | A fully functional request (ie. the resource was loaded successfully) |
| 4 | A client-side error. The most common codes span 400 to 404. For example, a 403 error means Forbidden, which means the visitor did not have the necessary permissions to access a resource, such as a specific page. |
| 5 | A server-side error. The most common codes span 500 to 510 For example, a 503 error means Server Unavailable, which means the server was unavailable, either overloaded or down for maintenance. |